
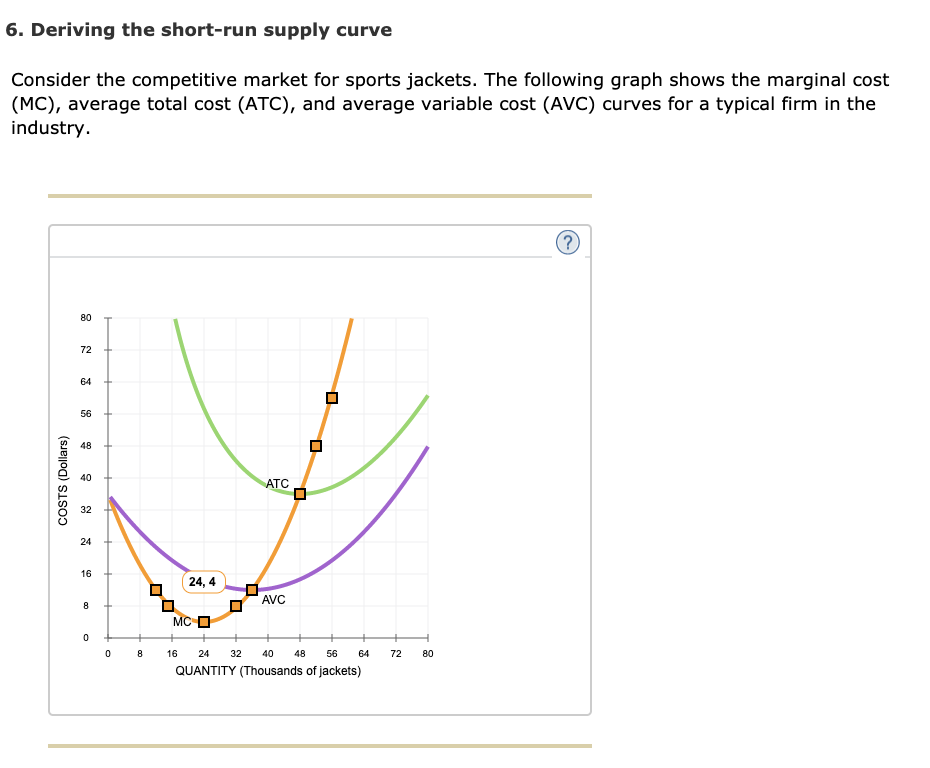
Marginal Revenues and Marginal Costs at the Raspberry Farm The equilibrium price of raspberries is determined through the interaction of market supply and market demand at $4.00. Marginal Revenues and Marginal Costs at the Raspberry Farm: Raspberry Market. The marginal cost (MC) curve is sometimes first downward-sloping, if there is a region of increasing marginal returns at low levels of output, but is eventually upward-sloping at higher levels of output as diminishing marginal returns kick in. For a perfectly competitive firm, the marginal revenue (MR) curve is a horizontal straight line because it is equal to the price of the good, which is determined by the market, shown in Figure 3. Marginal Revenues and Marginal Costs at the Raspberry Farm: Individual Farmer. You will notice that what occurs on the production side is exemplified on the cost side. The firm’s profit-maximizing choice of output will occur where MR = MC (or at a choice close to that point).

If the firm is producing at a quantity where MC > MR, like 90 or 100 packs, then it can increase profit by reducing output because the reductions in marginal cost will exceed the reductions in marginal revenue.
If the firm is producing at a quantity where MR > MC, like 40 or 50 packs of raspberries, then it can increase profit by increasing output because the marginal revenue is exceeding the marginal cost. But then marginal costs start to increase, displaying the typical pattern of diminishing marginal returns. In the raspberry farm example, shown in Figure 2, Figure 3 and Table 3, marginal cost at first declines as production increases from 10 to 20 to 30 packs of raspberries-which represents the area of increasing marginal returns that is not uncommon at low levels of production. Ordinarily, marginal cost changes as the firm produces a greater quantity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
